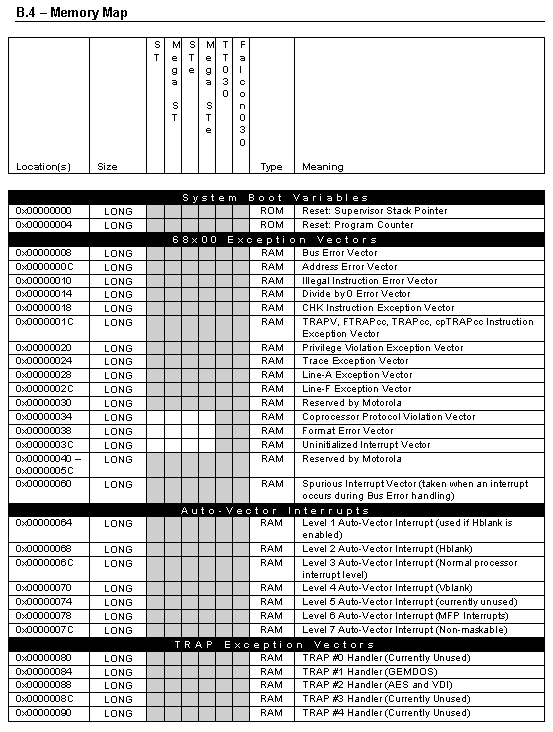
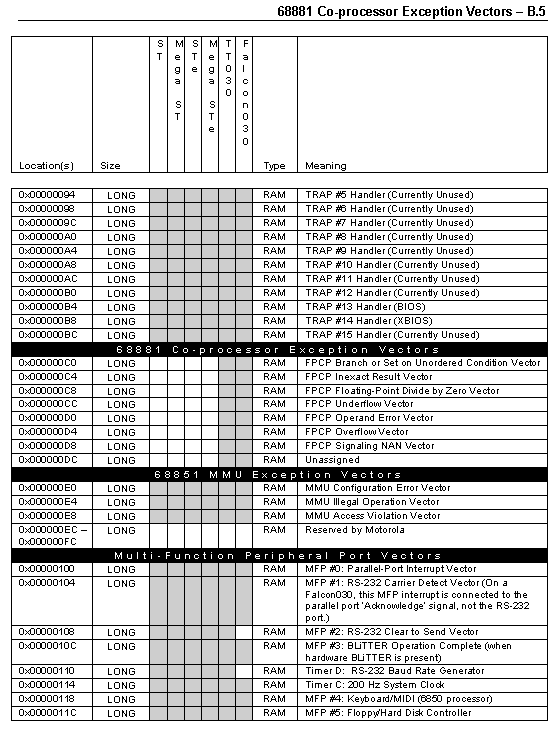
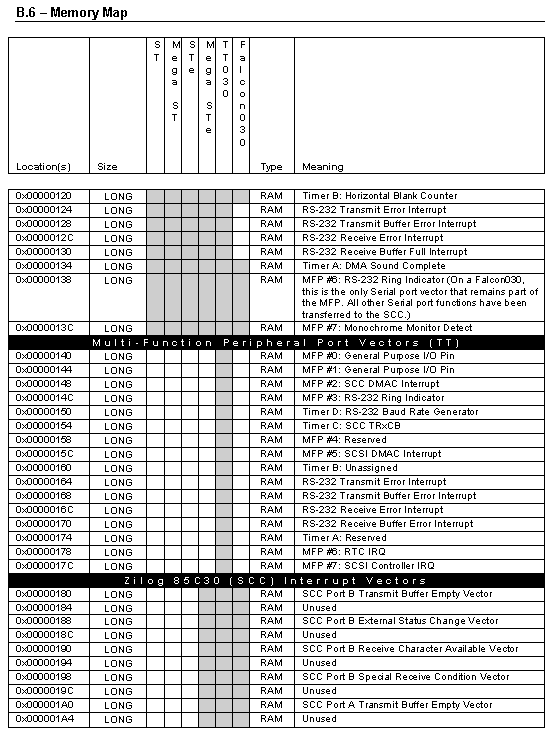
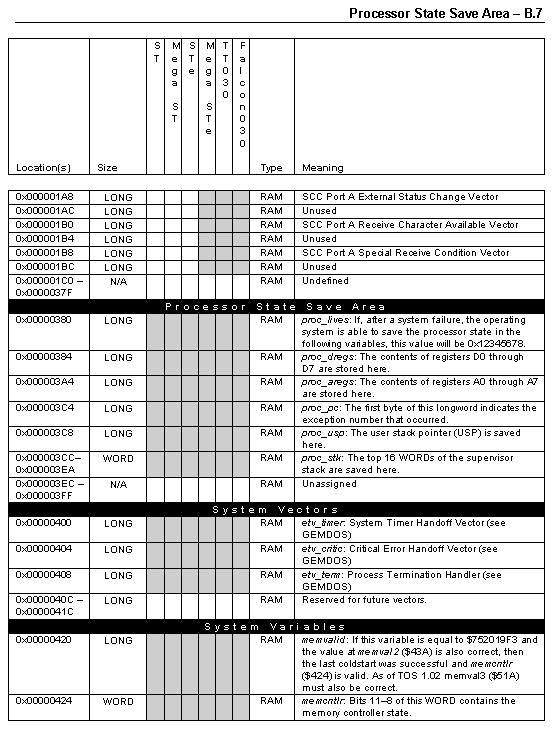
The information in this appendix provides a useful reference to the memory locations of the Atari computer series. While most documented locations have stayed backwardly compatible, some have changed in meaning. Software programmers directly accessing these locations should carefully consider the possibility that a location may move or not even exist in a newer version of the OS. For this reason many OS functions exist to manipulate system variables, vectors, interrupts, and devices. These should always be used, if possible, as an alternative to directly accessing hardware registers, vectors, interrupts, and variables.
|
|
Occupies one byte (8 bits). |
|---|---|
|
|
Occupies one WORD (16 bits). |
|
|
Occupies one longword (32 bits). |
|
|
Occupies the odd WORD of a LONG. |
|
|
Occupies the even WORD of a LONG. |
|
|
Occupies the odd BYTE of a WORD. |
|
|
Occupies the even BYTE of the WORD. |
|
|
Location is Read-Only Memory |
|
|
Location is Read-Write Memory |
|
|
Location is hardware-mapped |
|
|
Location addresses VME address space |
|
|
Not applicable |
|
|
Read-only location |
|
|
Write-only location |
|
|
Read-write location |
|
|
Reserved |
|
|
Either not assigned or undocumented (hardware developers should always consult Atari before mapping a third-party device to a hardware location). |



